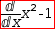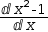3.6.4 Convert to Differential
If the subject is a subexpression of an equation,
the active expression is converted to a differential equation by using the subject
as the derivator and the expressions on either side as the
derivands of two derivative expressions.
Since there is only one subject, both derivatives will have the same derivator.
For example, the equation and selection 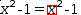
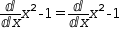
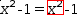
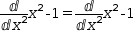
If the subject is a division operator whose operands are both decoupled derivatives,
the subject is transformed to a coupled derivative using the operand of the numerator
as the derivand and the operand of the denominator
as the derivator. That is, 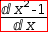
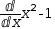
If the subject is a coupled derivative, it is transformed to a division of
decoupled derivatives using the derivand as the operand of the decoupled derivative in the numerator
and the derivator as the operand of the decoupled derivative in the denominator.
. That is,